Polytone K-Series resins in polyurethane (PU)
Ketonic Resin are also known as:
- Polyketone
- Ketone Aldehyde Resin
- Ketone Formaldehyde Resin
- Cyclohexanone Formaldehyde Resin
Some Basic Facts:
- Not functional in Water Based products.
- It can be used “BASE” Resin”
- It can be used a “BINDER”
- It’s used as “ADDITIVE” or “ENHANCER” or “MODIFIER” in formulation
- It turns “yellow” with time due to oxidation
- It is “hygroscopic” (attracts water)
| Inks -Any Solvent Based |
Polyurethane (PU) |
Nitrocellulose Based |
| Ball Pen Inks |
Inks |
Coating |
| Liquids Inks |
Coatings |
Sealant |
| Flexographic Inks |
Polyol Formulator |
Polish |
| Rotogravure Inks |
Flooring |
Adhesive |
| Packaging Inks |
PU Laminates |
|
| Surface Coatings |
Metallic Inks |
Paints (Rare) |
| Polish – Wood |
Cigarette Packaging |
Any Solvent Based |
| Paper Coating (Cards) |
Wrapper (Non Food) |
|
| Varnish |
|
|
PU Applications: Flooring, Construction & Wood

PU Applications: Pipe Coating: Water, Oil & Gas

PU applications Inks.
Polyurethane based Inks.
- Pu Based inks are applicable on polyester, BOPP, Nylon, Cellophane & PVDC coated films.
- PU based inks are suitable for solvent base/ solvent less/ PP Extrusion Lamination
- PU based inks can be further classified in to three categories depending upon solvent system used
- Toluene & MEK Based inks
- Toluene Free Inks
- Toluene & MEK Free Inks
PU applications Inks
- PU Inks has Excellent Printability and Resolubility.
- PU Inks has very good Adhesion on most of the substrate.
- They are High speed Printing Inks.
- PU Inks has very good Lamination Bond strength and extremely low Solvent Retention.
- Suitable for Boil and Retort Application.
About Polyurethan (PU)
- Developed by Otto Bayer in 1937
- Produced as Elastomers, Foams, Coatings, Adhesives Fibers, Synthetic Leather etc
- PU industry shown significant growth in adhesives and coatings
- Normally consists of Polyol (Polyester or Polyether Type, Isocynate & additive
- Property depends on Stoichiometric proportions of types of isocynates & polyols
- Oldest Type are 1-component PU system based on di- or triisocyanates that cured by reacting with active hydrogen on substrate or moisture

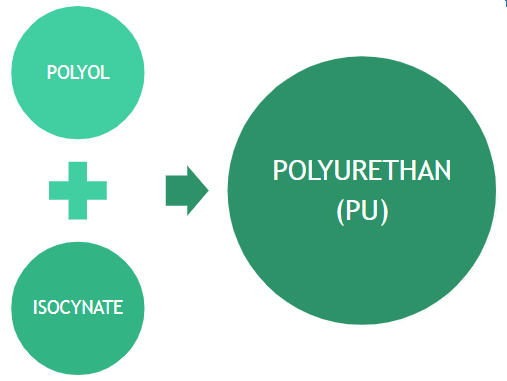
About Polyurethane/PU
Before we get too Technical! Basic of Polyurethane (PU System)
It’s a 2 Component System – it needs two reactants to make a PU
- PU can be Foam, Coatings, Adhesives, Fibers etc
When they say it is a 1 component system
- Moisture (water) plays the part(role) of the POLYOL
There are different types of Polyols & Isocyanates
- Choice of these different types determine the property of the final PU
- The “Reactive Sites or Groups” in the Polyol & Isocyanate reacts to produce the PU
Before we get too Technical! Basic of Polyurethane (PU System)
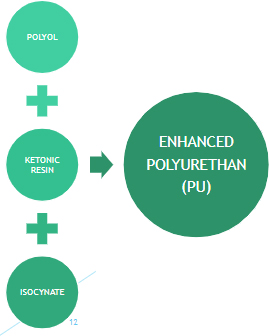
Where does Ketonic Resin come into the picture
- Ketonic resin can be mixed with Polyol and reacted with Isocyanate
- KR can be made into solution (e.g.mixed in chloroform) and reacted
- The solvent shall be needed to be removed by vacuum
Because KR has the same “Reactive Site/Group” as a Polyol
- It blends easily with Polyol
- It reacts easily with Isocyanate
- It gives enhancement in the overall property of the PU
- Basically its an additive which provides multiple benefits
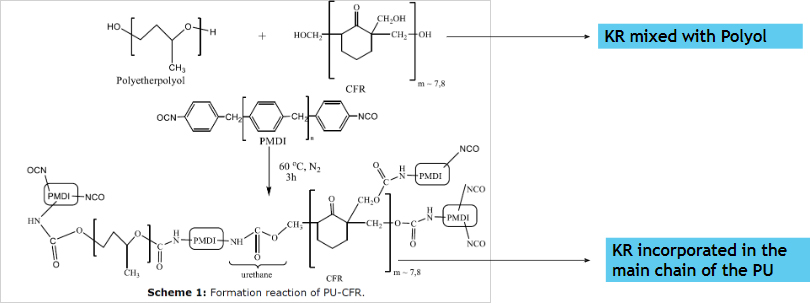
PU Systems with Ketonic Resin
KR interaction with PU System
Polyurethane Resins
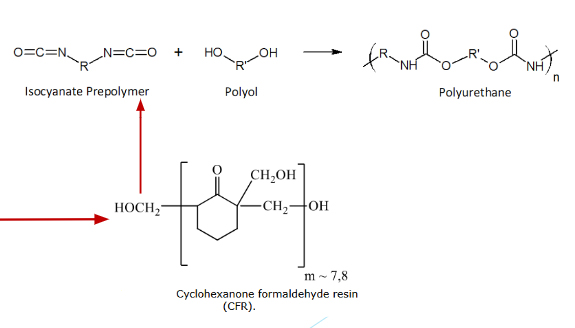
Resins such as Ketone Resin which contain hydroxyl groups are also used for modification of (for example PUR) binders. Our Ketone Resins “urethane grade” react easily with mono and di-isocyanates, such as HDI, TDI, MDI and IPDI. Different combinations of polyols and rnodifiedketone resin are used for ‘PUR system. Highly active hydroxyl group can react with isocyanate to improve the resistance to water, heat and corrosion. This technology is used In a wide variety of applications including indoor and outdoor floor coatings.
PU Systems with Ketonic Resin
KR interaction with PU System
- Resins such as POLYTONE K 96 and POLYTONE K 97 contain a high level of hydroxyl groups that makes it particularly suitable for combined use with polyols and isocyanates in the formulation of bicomponent polyurethane systems (PU or PUR 2K).
- Our Ketonic resins react easily with mono and di-isocyanates, such as HDI, TDI, MDI and IPDI.
- The strong bond created by hydroxyl group and isocyanates guarantees a strong resistance to water, heat and corrosion.
- This technology is used in a wide variety of applications including indoor and outdoor floors (for example : industrial plants, warehouses, garages, car parks, etc.) as well as roofs.
- The almost infinite possibility of combining colours and patterns makes these systems particularly suitable for finishing floors in designer shops and houses, where the only limit is the designer’s imagination.
KR interaction with PU System
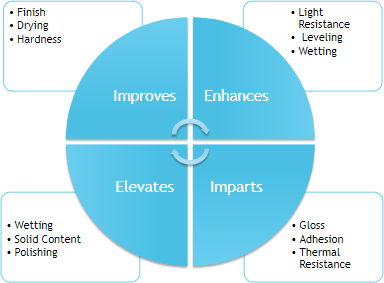
Benefits of KR in PU Systems
Ketonic Resin in Polyurethane
| Why Use Ketonic Resin? |
What is the effect and/or How it imparts? |
| As a Carrier or Binder |
Links with Polyol and reacts with IsoCyanide |
| As Flow Modifier |
-OH Value reacts and increases viscosity |
| Corrosion Prevention |
Low Acid Value |
| Color Fastness |
Binding Property-Binds Pigment+Solvent |
| Adhesion, Gloss |
Improves Adhesion to substrate |
| Increase Solid Content |
Resin is solid |
| Leveling |
Inherent Property |
| Hardness |
Resin isInherent Property solid |
| Gloss |
KR inherent property of gloss is imparted |
| Thermal Resistance |
KR increases Thermal Resistance |
| Green or Build Up Strength |
KR increses |
| Reduce NCO% |
Excess IsoCyanide is consumed by KR |
Characterisics – Effect On Formulation & End Product
KR products available
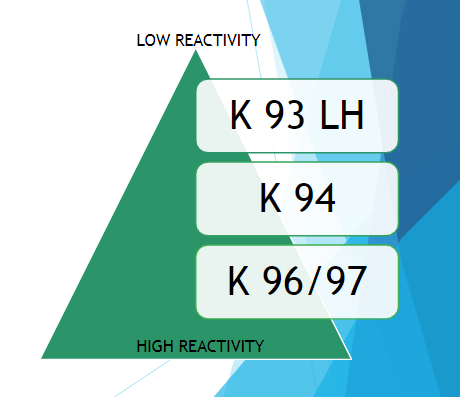
Which Product to Suggest
- Most well known product has been BASF’s Synthetic Resin CA
- Our POLYTONE K 94 is the direct equivalent of Synthetic Resin CA
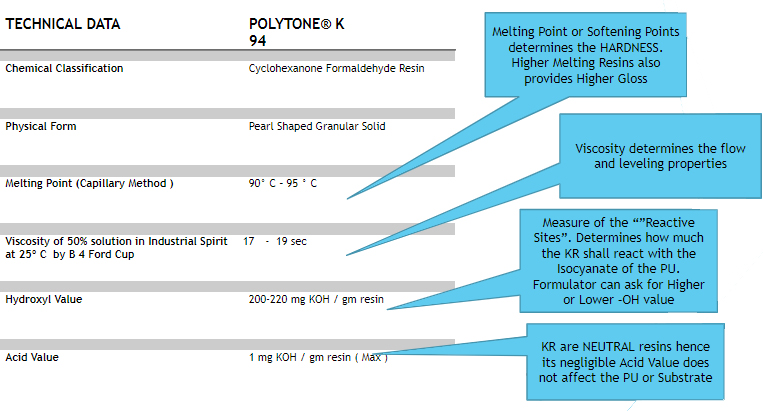
- The Hydroxyl Value (-OH Value) / Reactivity is 220-240
- Our LOW reactivity grade is K 93LH
- Low reactivity with Isocynates
- Used more as binder
- Our HIGH reactivity Grades are K 96/97, -OH Value upto 295
- High Reactivity with Isocyanates
- High Viscosity Changes, More Hardness
Characterisics – Effect On Formulation & End Product
| Parameters |
K 92LH |
K 93 |
K 93LH |
K 90 |
K 94 |
K 95 |
K 96 |
K 97 |
K 96 HH |
K 97 HH |
| Physical Form |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pale Yellow lumps |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
Pearl Shaped Granules |
| |
Low hydroxyl value grade |
Lump form |
Standard Grade |
High melting point grade |
High hydroxyl value grade |
| Softening point(Ball & Ring method)in deg c |
70-90 (very low) |
98-103 |
95-105 |
90-105 |
90-95 |
100-105 |
105-110 |
110-120 |
105-110 |
110-120 (very high) |
| Viscosity(B4 Ford Cup @ 25deg C)in sec(50% solution in spirit) |
14-19(very low) |
15-17 |
17-19 |
17-20 |
17-19 |
19-21 |
20-23 |
22-25 |
20-23 |
22-25(very high) |
| Hydroxyl Value(mg KOH/gm Resin) |
170-200(very low) |
265-285 |
170-200 |
170-220 |
200-220 |
230-250 |
230-250 |
230-250 |
270-295 |
270-295(very high) |
| Acid Value(mg KOH/gm Resin) |
<1 |
<1 |
<0.2% |
<1 |
<1 |
<1 |
<0.5% |
<0.5% |
<0.5% |
<0.5% |






















